- Thread Cutting
- Thread Forming
- Thread milling
Thread cutting taps are the most common tools for realizing the female thread. Cutting taps have only few requirements on the machine side and thanks to a large choice of tools there is a solution for any material and any application.
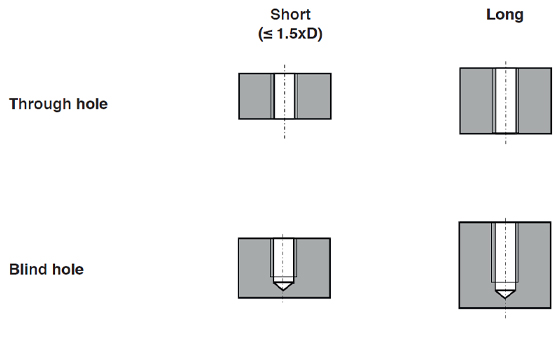
Types of hole
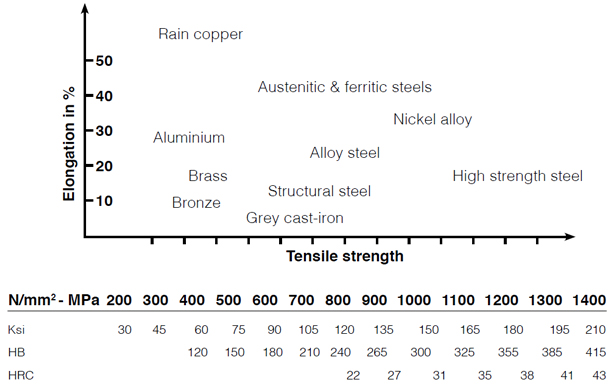
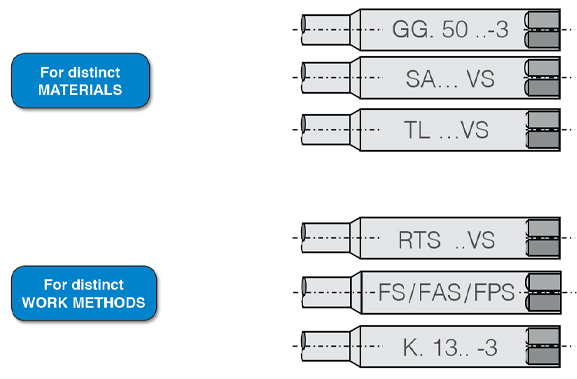
Materials
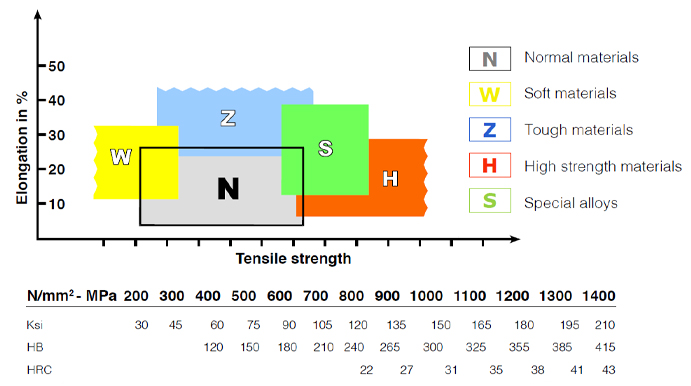
Tap Geometry
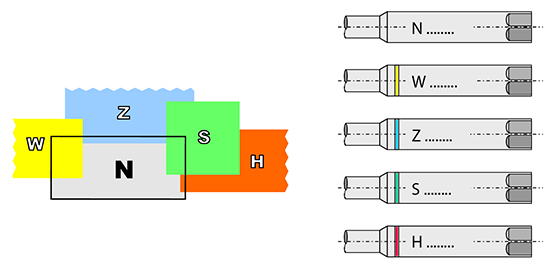
Tap Selection
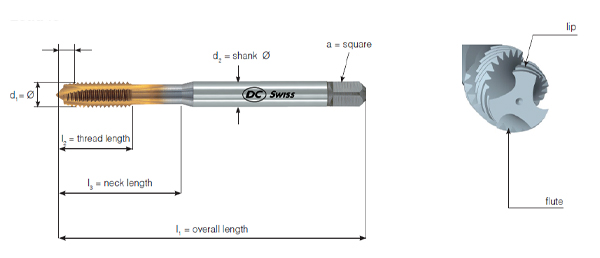
Tap dimension
Coating

Thread forming is a consistent solution for realizing the internal thread. The swarf remains the biggest opponent when cutting the thread and its evacuation, especially in deep threads and threads with counter-bore, is challenging. With the thread forming tap, the material will not be cut but formed. Thanks to the deforming process, the forming tap avoids creating swarfs or chips and guarantees a high process security with impressive performances.
Range of application
Range of application
All materials with a minimum of 10 % elongation and a tensile strength of up
to 1’150 N/mm2, e.g. steels, stainless steels, pure titanium, aluminium, copper, long chipping brass, etc.
Forming process
Forming process
The polished points and flats of the thread former’s teeth pierce the ductile material and force the material into the space in the tool profile. This creates
the thread profile with its typical groove in the crest.

Advantages
Advantages
- Higher process security due to the lack of shavings.
- Only one tool for both, through and blind holes.
- Optimal for deep threads.
- Thread with higher resistance of stripping by static and dynamic load.

Application restriction
Application restriction
For physical reasons, thread forming in thin-walled workpieces should be carried out with due care.

Adequate lubrication
Adequate lubrication
The thread forming process generates considerable friction. Therefore the tool must be protected by a film of lubricant. If the supply of lubricant is interrupted, then cold welding will quickly occur, resulting in tool failure.
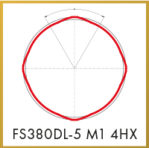
Thread former FS-DL
Thread former FS-DL
Universal thread former with 4 forming lobes for small thread sizes Ø ≥ 1 – < 3 mm, in all cold forming materials. With “DLC” wear-protective coating with
excellent lubrication and sliding properties. For stainless steels, pure copper, etc.
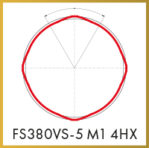
Thread former FS-VS
Thread former FS-VS
Universal thread former with 4 forming lobes for small thread sizes Ø ≥ 1 – < 3 mm, in all cold forming materials. With DC “VS” tool wear protective coating with high sliding properties.
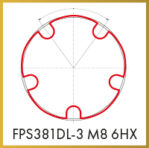
Thread former FPS-DL
Thread former FPS-DL
For Ø ≥ 3 mm, with large forming lobes designed for a progressive flow
of abrasive materials. With “DLC” wear-protective coating for better gliding and high tool life in long chipping brass and aluminium.
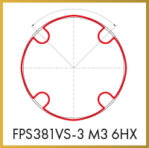
Thread former FPS-VS
Thread former FPS-VS
For Ø ≥ 3 mm, with large forming lobes designed for a progressive flow of materials with low elongation coefficient. With DC “VS” wear- protective coating with thermal and chemical properties. For structural steels, carbon steels, alloy steels, etc.
Thread former FAS-VS
Thread former FAS-VS
For Ø ≥ 3 mm, with pointed forming lobes designed for a fast flow of tough materials with high elongation coefficient. With DC “VS” wear-protective coating with excellent lubrication and sliding properties. For stainless steels, pure copper, etc

Lubrication grooves from Ø 3 mm
Lubrication grooves from Ø 3 mm
Lubricant will be guided to the surface of the tool which is directly in contact with the material.

Without lubrication grooves
Without lubrication grooves
Especially recommended for forming soft materials and for through holes in thin parts (e.g. for sheet metal working).

With internal coolant supply
With internal coolant supply
Highly recommended for deeper threads and for horizontal working.
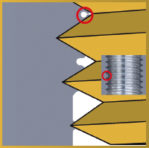
Correct thread profile
Correct thread profile
Accurate core hole is required in order to form a thread according to the norm.
For materials with a very high elongation coefficient and threading depth > 2 x D, we recommend increasing the core hole Ø by 0.02 to 0.05 mm.
Incorrect thread profile
Incorrect thread profile
Too big profile due to the too small core hole diameter. The required torque is higher. Incomplete profile caused by the core hole diameter being too big
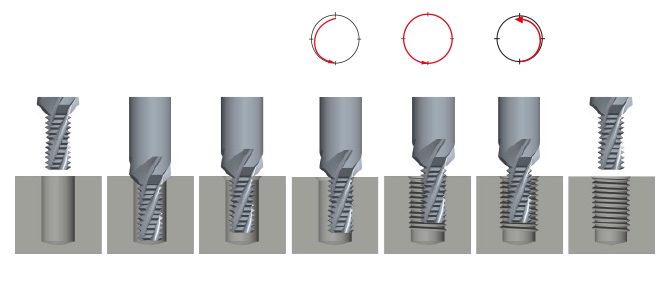
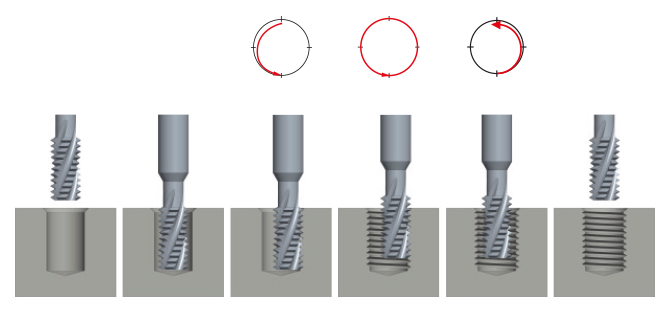
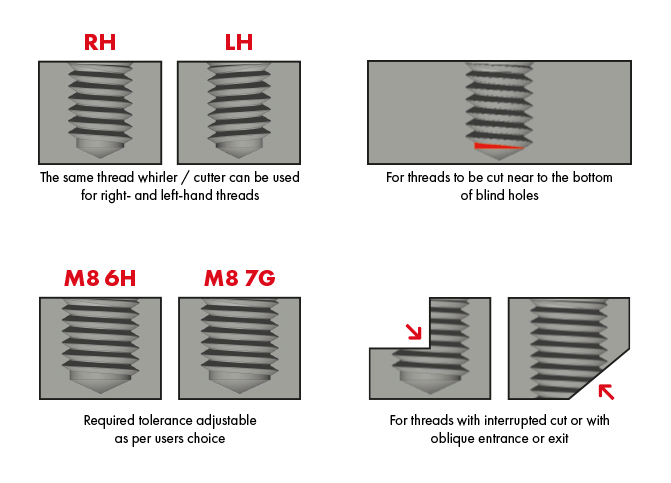
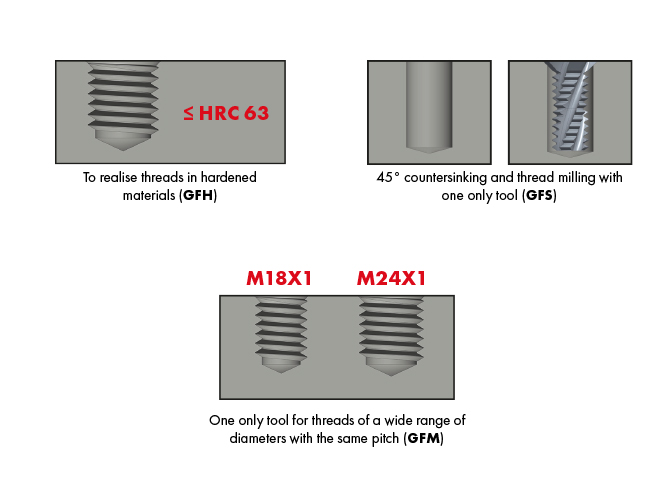
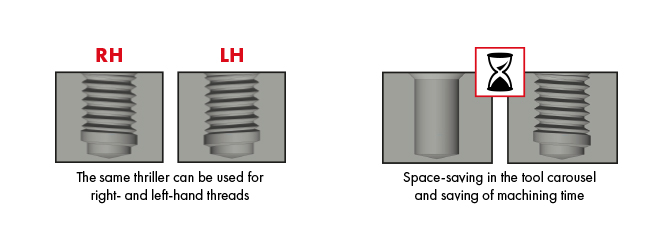
DC solid carbide thread milling cutters and thread whirl cutters for the easy manufacturing of through and blind holes, for right- and left-hand threads, with one only tool used on a stable CNC machine with 3-D-continuous path control.
The DC solid carbide thrillers are a further development of the standard thread milling cutters. Thanks to this combination tool with integrated drill, the core hole does not have to be pre-drilled separately first. The internal thread is cut in one operation, without changing the tool. All DC solid carbide drill thread milling cutters type BGF have internal cooling.
Requirements
- CNC machine with 3-D continuous path control
- Excellent machine stability
- Perfect concentricity of fixture
Program Overview

Programming cycle for thread milling cutters GF - GFH
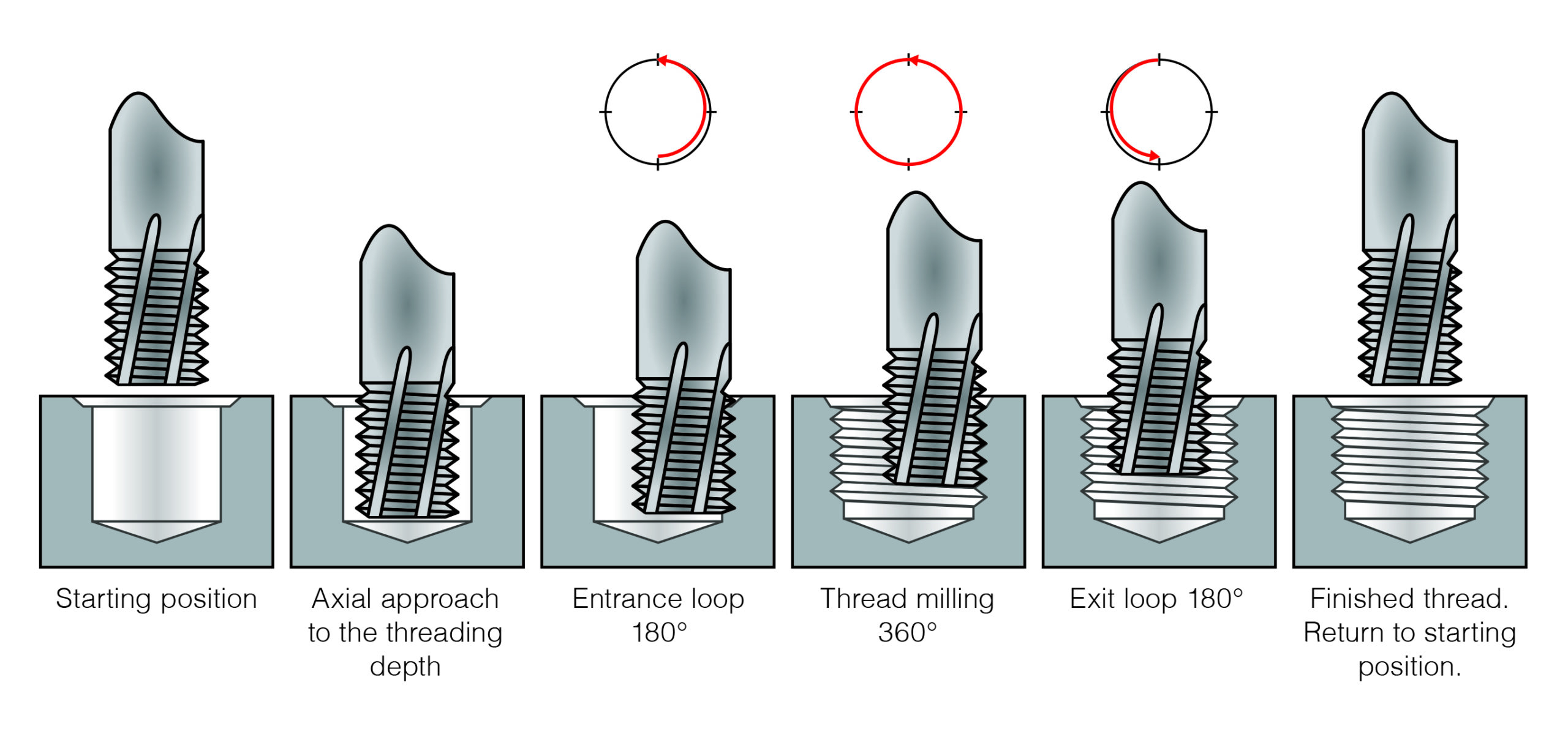
Programming cycle for thread milling cutters GFS
Programming cycle for thread milling cutters GFM
Specific application cases GF - GFH - GFS - GFM
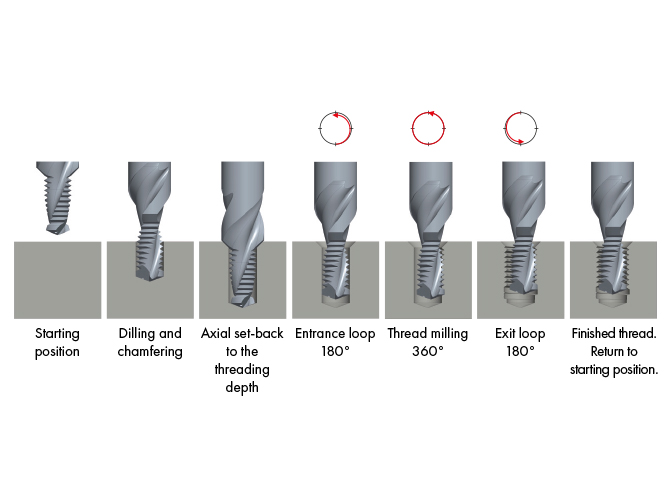
Thread milling Cycle / Operating Thread Thrilles BGF
Special executions BGF
Finders
Powerful search algorithms
Solutions
Our crafted solutions for every problem you might face
We guarantee economy of cost and extremely consistent, fault-free manufacture.
